6530-20-1 Metabolites; The study of chemical compounds extends beyond their initial chemical properties to include their metabolic processes within biological systems. Compound 6530-20-1, identified by its CAS number, is a subject of interest for understanding its metabolic pathways and the significance of its metabolites. These metabolic transformations can provide valuable insights into the compound’s pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, including how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. Furthermore, the study of metabolites is essential for evaluating the safety and potential toxicity of the compound, guiding drug development, and meeting regulatory requirements. By examining how 6530-20-1 interacts within biological systems and its resultant metabolites, researchers can better understand its therapeutic potential and safety profile.
Details Of Compound 6530-20-1 Metabolites
Chemical Identification: The CAS number for this compound is 6530-20-1 Metabolites, but its full IUPAC name or chemical structure would be referenced to detailed analysis trough a proper environmetal literature.
General Uses: Unique CAS numbers are also applied to compounds that serve a range of industries like pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and chemical manufacturing. Its uses largely depend on the chemical nature and properties of compound 6530-20-1 Metabolites.
5.1 Metabolism of Compound 6530-20-1 Metabolites
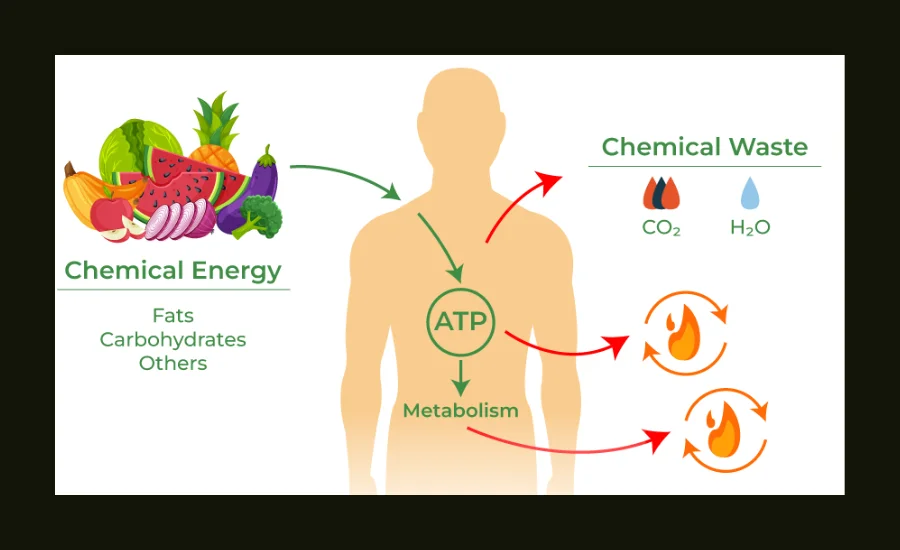
Metabolism: The sum of the biochemical processes within an organism that result in conversion from one compound into another (a metabolite). The most important metabolic pathways are Phase I and Phase II metabolism. Phase I metabolism typically makes the compound more hydrophilic to prepare them for reactions catalysed by other enzymes (phase II metabolism). This may be achieved by oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis of the compounds which introduce or unmask a functional group on the molecule. The phase II metabolism comprises conjugation reactions in which the compound, or its Phase I metabolites, is linked with endogenous compounds such as glucuronic acid (glucuronidation), sulfate and amino acids to increase their aqueous solubility for excretion.
Key Metabolites
The metabolites of the compound 6530-20-1 Metabolites that are created during these metabolic processes. The exact structure and properties of these intermediates are dictated by the chlorine-substituted compound in question. These are primarily what we will focus on, consist mainly of hydroxylated metabolites (adding one or two OH groups) and conjugated metabolite(such as the addition of glucuronic acid or sulfate).
Analytical Methods
The metabolites are quantified using advanced analytical techniques. Mass spectrometry (MS):A versatile tool for structureelucidation of glycosphingolipids by alina p. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy allows for the chemical structure of metabolites to be determined. Metabolomics utilizes High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) for the separation and quantification of metabolites present in a biological sample
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics

The study of metabolites formed from compound 6530-20-1 Metabolites is necessary for understanding pharmacokinetics (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion process) in the body as well as to elicit its next metabolic profile. This information is important to know due of the manner in which it influences how effective the compound will be within your body. Moreover, a few metabolites could exhibit the biological activity of parent molecule and thus affecting its therapeutic potential as well.
Safety and Toxicology
It is important to be aware of the metabolites, as it will help you understands how safe compound 6530-20-1 Metabolites happens to be. Occasionally a metabolite is also toxic giving rise to adverse effects and therefore unsuitability of the compound for clinical use. Additionally, bioactivation (whereby a compound is metabolized to an active derivative) can potentiate or change its effects so it is important to study these transformations as well.
Drug Development & Regulation
It is important in drug development to learn the things about metabolic profile of a compound that we are designing such medications which could be safer and more efficacious. Understanding the formation of metabolites allows researchers to modify drug structures in ways that allow them to be active against a disease but not through harmful metabolic processes. The safety and efficacy of new drugs must be established through extensive metabolic data before they are approved for therapeutic use by regulatory agencies to protect public health.
Final Words
Investigating the metabolites of compound 6530-20-1 Metabolites plays a crucial role in understanding its behavior and impact within biological systems. Insights into the compound’s metabolic pathways provide essential information about its pharmacokinetics, influencing its efficacy and safety. Identifying potential toxic metabolites and understanding the process of bioactivation are vital for ensuring the compound’s suitability for therapeutic use. In drug development, this knowledge guides the creation of safer and more effective drugs, while also fulfilling regulatory requirements. Ultimately, a thorough examination of metabolic processes contributes to optimizing the compound’s use and enhancing its benefits while minimizing risks.
For more information and updates join us on Discover thril



Leave a Reply
View Comments