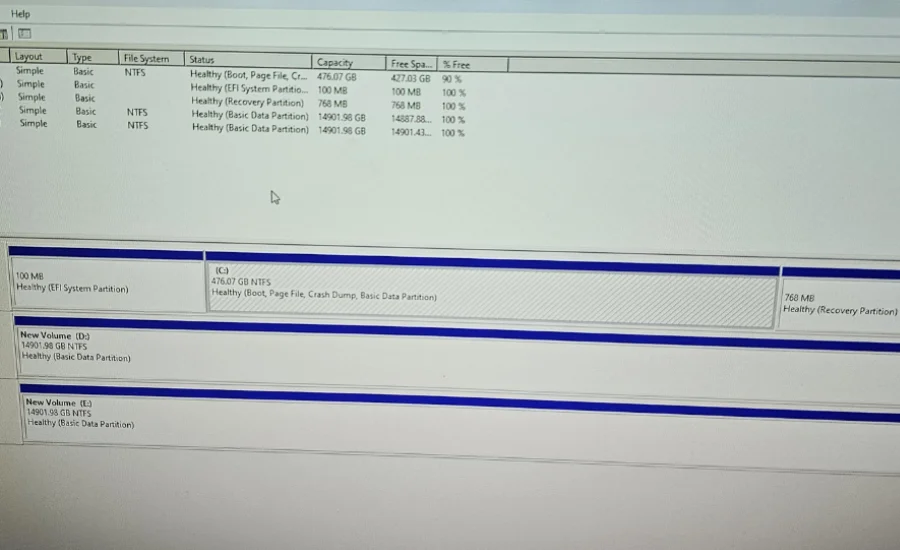
14901.98 to tb, is a significant unit of digital storage, representing approximately one trillion bytes (1,000,000,000,000 bytes). This expansive measurement is frequently used to quantify the capacity of substantial storage systems, including hard drives, servers, and cloud storage solutions. Terabytes play a crucial role in modern data management, particularly for handling large-scale digital content such as high-definition media files, comprehensive databases, and extensive data archives.
Converting Gigabytes to Terabytes
To effectively manage digital storage, it’s essential to understand how to convert between different units of measurement. The conversion from 14901.98 to tb is a common requirement. One terabyte is equivalent to 14901.98 to tb. This conversion factor reflects the binary system used in digital storage, where each unit is a power of 2.
To convert a given amount of gigabytes into terabytes, you use the following formula:
[ \text{Terabytes (TB)} = \frac{\text{Gigabytes (GB)}}{1,024} ]
For example, if you have 14,901.98 gigabytes, the conversion to terabytes would be:
[ \text{Terabytes} = \frac{14,901.98 \text{ GB}}{1,024} \approx 14.55 \text{ TB} ]
This result indicates that 14,901.98 gigabytes is approximately 14.55 terabytes, providing a clear understanding of how the storage capacity scales with larger units.
The Hierarchical Structure of Digital Storage
14901.98 to tb, To grasp data conversion from bytes to terabytes, it’s important to understand the hierarchical structure of digital storage units. Each unit increases by a factor of 1,024 compared to the previous one. This hierarchical structure is fundamental to data measurement and management. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- 1 Kilobyte (KB) = 1,024 Bytes
- 1 Megabyte (MB) = 1,024 Kilobytes
- 1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1,024 Megabytes
- 1 Terabyte (TB) = 1,024 Gigabytes
To convert bytes to terabytes, you use the formula:
[ 1 \text{ Terabyte (TB)} = 1,024^4 \text{ Bytes} = 1,099,511,627,776 \text{ Bytes} ]
Thus, to determine how many terabytes are in a given number of bytes, apply this conversion:
[ \text{Terabytes} = \frac{\text{Bytes}}{1,099,511,627,776} ]
Practical Conversion Example
Consider converting 14901.98 to tb. Using the standard conversion formula:
[ \text{Terabytes} = \frac{14,901.98 \text{ Bytes}}{1,099,511,627,776} ]
This yields:
[ \text{Terabytes} \approx 1.36 \times 10^{-8} \text{ TB} ]
This means that 14901.98 to tb is approximately (1.36 \times 10^{-8}) terabytes. While this number seems very small, it underscores the vast scale of storage units as you progress from bytes to terabytes.
The Importance of Accurate Conversion
14901.98 to tb, Understanding and performing accurate conversions between bytes and terabytes is essential for efficient data management and storage planning. Accurate conversion helps in:
- Assessing Storage Needs: By converting data into appropriate units, you can better estimate the storage requirements for projects, backups, and data archiving.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently managing storage resources, whether for personal use, enterprise environments, or cloud-based systems, relies on precise data conversion.
- Data Processing: For tasks such as database management, large-scale data analysis, and media production, knowing the correct storage capacity is crucial for optimal performance and organization.
Contextualizing Data Size
14901.98 to tb, When dealing with digital storage, converting data sizes to a more comprehensible unit is crucial for understanding their scale and impact. For instance, converting 14901.98 to tb results in approximately (1.36 \times 10^{-8}) terabytes. This number might seem abstract, so comparing it to more familiar quantities can provide a clearer perspective on its significance.
What is a Terabyte?
14901.98 to tb, is a vast unit of data storage, equating to approximately one trillion bytes (1,000,000,000,000 bytes). To put this in perspective:
- 250,000 high-resolution photos can be stored in one terabyte. This quantity represents a large digital photo collection, often accumulated over several years.
- 500 hours of high-definition video fit into a terabyte. This could cover the entirety of many TV series or a substantial collection of high-quality movies.
- 6.5 million pages of text can be accommodated within a terabyte. This volume is equivalent to a vast library or several comprehensive books.
Comparing 14901.98 to tb
In comparison to a terabyte, 14901.98 to tb is a minuscule amount of data. To give a more relatable comparison:
- Text Document: This is roughly equivalent to a brief text file containing a few sentences or a small note. For instance, a single-page text document might fall into this range.
- Low-Quality Audio: It can represent just a few seconds of compressed audio playback, such as a short sound clip or a brief voicemail message.
Practical Implications of Small Data Sizes
14901.98 to tb, Understanding small data sizes is important across several contexts:
- Data Transmission: When transmitting data over networks, knowing the size of small data packets can aid in optimizing network usage and improving data transfer efficiency. For example, small packets are often used in real-time communication and online transactions.
- Storage Allocation: For specific tasks that involve minimal storage requirements, such as storing configuration files or small system logs, understanding these small sizes helps in managing storage resources effectively.
- File Management: In personal and professional environments, accurately managing and organizing small files—like system logs or temporary files—is essential for maintaining a clutter-free and efficient digital workspace.
Expanding the Concept of Data Sizes
14901.98 to tb, Understanding and contextualizing data sizes extends beyond just managing storage. It plays a crucial role in:
- Personal Data Management: For individuals, knowing how much space different types of files consume helps in selecting appropriate storage solutions. This understanding guides decisions on whether to use local storage devices, external hard drives, or cloud storage services. For example, a person might choose a 1 TB external hard drive to store their extensive photo and video library, knowing it can accommodate hundreds of thousands of images and hours of video.
- Professional Data Management: In fields such as IT, data analysis, and digital media, recognizing data size conversions is essential for optimizing resources. For IT professionals, accurate data size knowledge is vital for planning and scaling infrastructure. In data analysis, understanding file sizes helps in managing large datasets and ensuring efficient data processing. For digital media professionals, knowing the storage requirements for high-resolution content ensures proper project planning and budget allocation.
Practical Applications of Data Conversion
Mastering data size conversions has broad implications across various sectors:
Accurate Storage Planning:
- IT Infrastructure: IT professionals rely on precise data conversions to forecast and allocate storage resources effectively. This ensures that servers, cloud storage solutions, and data centers have adequate space for current and future requirements. Effective planning prevents issues related to over-provisioning or under-provisioning of storage.
- Digital Media Production: Understanding storage needs for high-resolution images, videos, and audio files is crucial for project planning. It aids in selecting appropriate storage devices and managing production workflows efficiently.
- Streamlined Data Management:
- Data Analysis: Analysts benefit from a clear understanding of data sizes to enhance processing efficiency and optimize database performance. Knowing how data volumes impact processing times and storage requirements helps in designing efficient data architectures and retrieval systems.
- File Organization: Accurate size estimates assist in organizing digital assets effectively, minimizing clutter, and ensuring quick access to important files. This is particularly useful in environments with extensive file collections, such as research labs or media production studios.
- Optimized Hardware and Software Usage:
- Hardware Selection: Professionals can make informed decisions when selecting storage devices, such as SSDs, HDDs, or cloud solutions. Understanding data size requirements helps in choosing devices with appropriate capacities and performance characteristics.
- Software Efficiency: Knowledge of data sizes aids in selecting suitable software for tasks like data compression, transfer, and backup. Efficient use of software resources ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Broader Implications of Data Size Knowledge
- Network Management: 14901.98 to tb, Accurate data size knowledge is critical for predicting and managing data transfer demands. It helps in optimizing bandwidth usage and ensuring reliable network performance. This is crucial for maintaining efficient network systems, particularly in high-traffic environments.
- Personal Data Management: On an individual level, understanding data sizes aids in managing digital libraries effectively. It ensures that devices have adequate space for applications, media, and documents, preventing issues related to storage overflow and ensuring smooth operation.
To explore the future of a data size of 14,901.98 bytes when considering its conversion to terabytes and its implications, we should look at several key aspects:
Current Context
At present, 14,901.98 bytes is an extremely small amount of data, especially when compared to the scale of a terabyte. Specifically, 14,901.98 bytes equates to approximately (1.36 \times 10^{-8}) terabytes. This tiny fraction of a terabyte is comparable to a brief text document or a few seconds of low-quality audio.
Future Considerations
As technology advances and data management needs evolve, here’s how the future might impact the context of such small data sizes:
1. Data Growth and Storage Need
- Increased Data Volumes: As digital data continues to proliferate, the relevance of very small data sizes like 14,901.98 bytes might diminish in the context of massive datasets. While this size will remain small, it will be part of increasingly larger data ecosystems where even small data fragments contribute to overall storage needs.
- Storage Solutions: Future storage technologies, such as more advanced SSDs, next-generation cloud storage, and emerging storage mediums, will continue to handle vast amounts of data efficiently. While individual data sizes will still be small in comparison to these technologies, the importance of accurately managing and understanding even these tiny data pieces will persist.
2. Data Management and Analysis
- Enhanced Data Compression: Future advancements in data compression technologies could make managing small data sizes more efficient, enabling even finer granularity in data handling. These improvements will ensure that every byte, no matter how small, is managed optimally.
- Big Data Integration: As big data analytics tools evolve, they will increasingly incorporate and analyze vast quantities of small data points. Understanding the role of even minute data sizes will be crucial in extracting valuable insights from large datasets.
3. Emerging Technologies
- Quantum Computing: As quantum computing progresses, the way we handle and process data might change dramatically. Quantum computing could potentially revolutionize data management by processing enormous amounts of data rapidly, making small data sizes less of a concern in the context of overall computing power.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning technologies will likely continue to advance, improving how small data fragments are used in training models and making sense of massive datasets. Understanding even small amounts of data will contribute to more sophisticated AI systems.
4. Personal and Professional Use Cases
- Personal Storage Solutions: For individual users, the future may bring more personalized storage solutions that better manage small data sizes within larger datasets. Improved user interfaces and storage management tools will help individuals make better use of their available space.
- Professional Data Management: In professional settings, particularly in data-intensive fields such as data science, healthcare, and financial services, managing small data sizes will be integral to handling large-scale data processes and ensuring data integrity.
Final Words
Understanding the conversion from 14901.98 GB to TB is crucial for effective digital storage management. With approximately 14.55 TB, this significant unit of measurement highlights the expansive capacity required for handling large-scale digital content, such as high-definition media, comprehensive databases, and extensive data archives. Accurate conversions between units like gigabytes and terabytes are essential for assessing storage needs, optimizing resource allocation, and managing data efficiently. As data continues to grow exponentially, mastering these conversions will remain vital for both personal and professional applications, ensuring seamless data management and system performance.
Discover valuable insights and tips at DiscoverThrill to stay informed.







Leave a Reply
View Comments